报了个 每日一题 希望能坚持下去
day01
统计子矩阵
一眼前缀和+二分
t到怀疑人生
从一开始枚举左上角端点就是个错误
因为当左端点确定后,边界线差不多是这样的
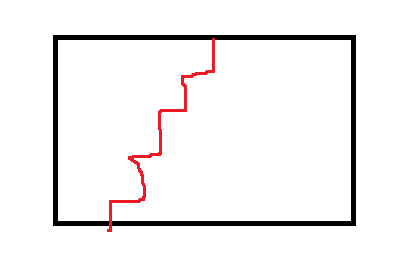
那么这种思路的复杂度就会被卡死在 $n^3logn$ 嘤嘤嘤
题解用了一种很神奇的方法,枚举上边界和下边界,在边界中寻找左右端点
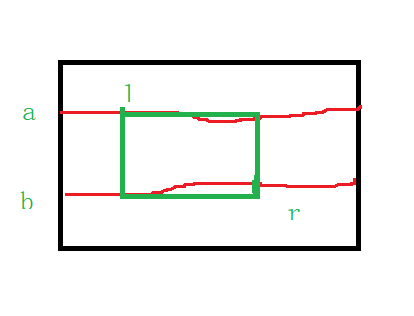
图中(a,l) (b,r)区间内的点即为所求
用双指针就可以把复杂度降到 $n^3$
真神奇
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define bug(x) cout<<#x<<"x="<<x<<endl
using namespace std;
const int maxx = 500 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + ch - 48;
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
int a[maxx][maxx]={0};
signed main() {
int n,m,k;
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
cin>>a[i][j];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
a[i][j]+=a[i-1][j]+a[i][j-1]-a[i-1][j-1];
int cnt=0;
for(int u=1;u<=n;u++)
for(int d=u;d<=n;d++)
for(int l=1,r=1;r<=m;r++)
{
while(l<=r&&a[d][r]-a[u-1][r]-a[d][l-1]+a[u-1][l-1]>k) l++;
if(l<=r) cnt+=r-l+1;
}
cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
|
题解里有一维优化,大概就是求出每一列前缀和,每次加减都是以 (u,d) 区间内的某一列进行的
想了一下感觉好像不会快很多的样子,而且也不存在空间优化…懒得写了
day02
最多能完成排序的块 II
单调栈
维护每个区间的最大值,如果 x> max ,则x单独成为一个区间
否则需要找到 x 可以插入的区间 (区间合并直到成为第一个区间或者前一个区间的最大值不超过x)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public:
int maxChunksToSorted(vector<int>& arr) {
stack<int> st;
for(auto i:arr)
{
if(st.empty()||st.top()<=i)
st.push(i);
else
{
int m=st.top();
while(!st.empty()&&st.top()>i) st.pop();
st.push(m);
}
}
return st.size();
}
};
|
day03
用户分组
快乐模拟
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> groupThePeople(vector<int>& groupSizes) {
map<int,vector<int>> mp;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int l=groupSizes.size();
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if(mp.find(groupSizes[i])==mp.end())
{
vector<int> a;
a.push_back(i);
mp[groupSizes[i]]=a;
}
else mp[groupSizes[i]].push_back(i);
if( mp[groupSizes[i]].size()==groupSizes[i])
{
vector<int> b;
ans.push_back(mp[groupSizes[i]]);
mp[groupSizes[i]]=b;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
|

