果然每次写博客都是因为发现自己太菜
不过二叉树确实很难写到
最近写天梯赛发现自己不会 就学一下吧
二叉树
给出前序中序 求二叉树
分治 + 递归
建立前序和中序对于同一节点的对应关系
递归中序遍历
先找父节点(通过与前序的对应关系)
然后递归左子树和右子树
1
2
3
4
5
| if(l>r) return null;
int x =mp[pre[fa]];
pa->left=so(fa+1,l,x-1);
pa->r=so(fa+x-l+1,x+1,r);
|
题目链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int pre[35] = { 0 }, ino[35] = { 0 };
struct no {
int num, ls, rs;
};
no cnm[35];
map<int, int> mp;
int n;
vector<int> ans;
int cnt = 0;
int so(int p,int fa, int l, int r)
{
if (l > r) return -1;
int x = mp[pre[fa]];
cnm[p].num = pre[fa];
cnt++;
cnm[p].ls=so(cnt,fa + 1, l, x - 1);
cnt++;
cnm[p].rs=so(cnt,fa + x - l + 1, x + 1, r);
return p;
}
void sh()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
while (!q.empty())
{
int fa = q.front(); q.pop();
if (cnm[fa].rs != -1) q.push(cnm[fa].rs);
if (cnm[fa].ls != -1) q.push(cnm[fa].ls);
ans.push_back(cnm[fa].num);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i) cout << " ";
cout << ans[i];
}
return;
}
signed main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> ino[i], mp[ino[i]] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> pre[i];
so(cnt,0, 0, n - 1);
sh();
return 0;
}
|
给后序和中序 求二叉树
跟上一种情况一样
题目链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int pos[35] = { 0 }, ino[35] = { 0 };
map<int, int> mp;
struct no {
int num, ls, rs;
};
no cnm[100];
vector<int> ans;
int n, cnt = 0;
int so(int p, int fa, int l, int r)
{
if (l > r) return -1;
int x = mp[pos[fa]];
cnm[p].num = pos[fa];
cnt++;
cnm[p].ls = so(cnt, fa+x-r-1, l, x - 1);
cnt++;
cnm[p].rs = so(cnt, fa - 1, x + 1, r);
return p;
}
void sh()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
while (!q.empty())
{
int fa = q.front(); q.pop();
if (cnm[fa].ls != -1) q.push(cnm[fa].ls);
if (cnm[fa].rs != -1) q.push(cnm[fa].rs);
ans.push_back(cnm[fa].num);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i) cout << " ";
cout << ans[i];
}
}
signed main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> pos[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> ino[i], mp[ino[i]] = i;
so(0, n-1, 0, n - 1);
sh();
return 0;
}
|
给完全二叉树的后序遍历 求二叉树
这个直接推比较麻烦,由于是完全二叉树,可以直接遍历
相当于先跑出节点个数为n的完全二叉树的后序遍历,然后把对应的数字填进去
题目链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[35];
int n;
void dfs(int x)
{
if(x>=n) return ;
dfs(x*2+1);
dfs(x*2+2);
cin>>a[x];
}
signed main()
{
cin>>n;
dfs(0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(i) cout<<" ";
cout<<a[i];
}
return 0;
}
|
二叉搜索树
一棵二叉搜索树可被递归地定义为具有下列性质的二叉树:对于任一结点,
- 其左子树中所有结点的键值小于该结点的键值;
- 其右子树中所有结点的键值大于等于该结点的键值;
- 其左右子树都是二叉搜索树
给出前序遍历问是否为二叉搜索树并还原
题目链接
先不考虑镜像情况
根据二叉树的前序遍历和二叉搜索树的性质 有
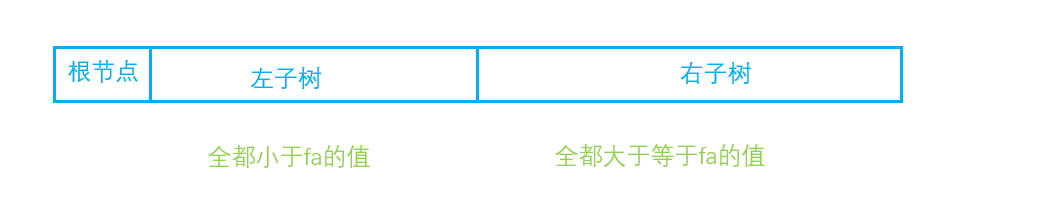
所以左子树区间为 ( fa + 1 , x ) x 为从右向左数第一个小于fa值的数的下标
右子树区间为 ( y , r ) y为从左向右数第一个大于等于fa值的数的下标
并且x == r || y == fa+1 || x == y-1 //无右子树 无左子树 有左右子树
然后递归求解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[1005];
int n;
vector<int> ans;
bool s1(int l,int r)
{
if(l>r) return 1;
int fa=l;
l++;
int x=r,y=l;
while(x>=l&&a[x]>=a[fa]) x--;
while(y<=r&&a[y]<a[fa]) y++;
bool f=1,ff=1;
if(x>r||y<l) f=s1(fa+1,r);
else
{
if(y!=x+1) return 0;
f=s1(fa+1,x);
ff=s1(y,r);
}
ans.push_back(a[fa]);
return f&&ff;
}
bool s2(int l,int r)
{
if(l>r) return 1;
int fa=l;
l++;
int x=r,y=l;
while(x>=l&&a[x]<a[fa]) x--;
while(y<=r&&a[y]>=a[fa]) y++;
bool f=1,ff=1;
if(x<l||y>r) f=s2(fa+1,r);
else
{
if(y!=x+1) return 0;
f=s2(fa+1,x);
ff=s2(y,r);
}
ans.push_back(a[fa]);
return f&&ff;
}
void sh()
{
cout<<"YES\n";
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(i) cout<<" ";
cout<<ans[i];
}
return;
}
signed main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
if(s1(0,n-1)) {sh();return 0;}
ans.clear();
if(s2(0,n-1)) {sh();return 0;}
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
|
给一个序列插入二叉搜索树求树的结构
就直接模拟完事
题目链接1
如何判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
对于层序遍历结果而言,找到第一个不饱和节点后,后续的节点全没儿子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct no{
int num,ls,rs;
};
no cnm[25];
void so(int fa,int i)
{
if(cnm[fa].num<cnm[i].num)
{
if(cnm[fa].ls==-1) {cnm[fa].ls=i;return ;}
else so(cnm[fa].ls,i);
}
else
{
if(cnm[fa].rs==-1){cnm[fa].rs=i;return ;}
else so(cnm[fa].rs,i);
}
return;
}
bool sh()
{
vector<int> ans;
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
while(!q.empty())
{
int fa=q.front();q.pop();
if(cnm[fa].ls!=-1) q.push(cnm[fa].ls);
if(cnm[fa].rs!=-1) q.push(cnm[fa].rs);
ans.push_back(fa);
}
int l=ans.size();
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if(i) cout<<" ";
cout<<cnm[ans[i]].num;
}
int i = 0;
for (; i < l; i++)
{
if (cnm[ans[i]].ls != -1 && cnm[ans[i]].rs != -1);
else break;
}
if(cnm[ans[i]].ls==-1&&cnm[ans[i]].rs != -1) return 0;
i++;
for (; i < l; i++)
if (cnm[ans[i]].ls != -1 || cnm[ans[i]].rs != -1) return 0;
return 1;
}
signed main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>cnm[i].num,cnm[i].ls=cnm[i].rs=-1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
so(0,i);
if(sh())
cout<<"\nYES";
else cout<<"\nNO";
return 0;
}
|
题目链接2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct no {
int num, ls, rs, c, fa;
};
map<int, int> mp;
no cnm[105];
void so(int fa, int i)
{
if (cnm[fa].num > cnm[i].num)
{
if (cnm[fa].ls == -1) { cnm[fa].ls = i; cnm[i].fa = fa; cnm[i].c = cnm[fa].c + 1; return; }
else so(cnm[fa].ls, i);
}
else
{
if (cnm[fa].rs == -1) { cnm[fa].rs = i; cnm[i].fa = fa; cnm[i].c = cnm[fa].c + 1; return; }
else so(cnm[fa].rs, i);
}
return;
}
string s;
int to_num(int& i)
{
int l = s.size();
int x = 0;
int ff = 1;
for (; i < l; i++) if (s[i] <= '9' && s[i] >= '0' || s[i] == '-') break;
if (s[i] == '-') ff = -1, i++;
while (i < l && s[i] <= '9' && s[i] >= '0')
{
x = x * 10 + s[i] - '0';
i++;
}
return x * ff;
}
signed main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> cnm[i].num, mp[cnm[i].num] = i, cnm[i].ls = cnm[i].rs = -1;
cnm[1].fa = 0, cnm[1].c = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
so(1, i);
int m;
cin >> m;
getchar();
while (m--)
{
int a, b, i = 0;
getline(cin, s);
if (s.find("root") != string::npos)
{
a = to_num(i);
if (mp[a] == 1) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
else
{
a = to_num(i);
b = to_num(i);
if (!mp[a] || !mp[b]) { cout << "No\n"; continue; }
if (s.find("siblings") != string::npos)
{
if (mp[a] != mp[b] && cnm[mp[a]].fa == cnm[mp[b]].fa)cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
else if (s.find("parent") != string::npos)
{
if (cnm[mp[b]].fa == mp[a])cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
else if (s.find("left") != string::npos)
{
if (cnm[mp[b]].ls == mp[a]) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
else if (s.find("right") != string::npos)
{
if (cnm[mp[b]].rs == mp[a]) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
else if (s.find("level") != string::npos)
{
if (cnm[mp[a]].c == cnm[mp[b]].c)cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
}
}
return 0;
}
|
