题单链接
emmm
觉得一篇篇写起来太复杂了
把这个整合起来比较方便
2022.03.28 18:06
完结撒花
1~10 数组中重复的数字 思路1 这种题目当然要用set啦
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 set <int > s;for (auto x:nums)if (s.count (x)) return x;insert (x);return -1 ;
思路2 set能做到的东西map肯定也行啊
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 map <int ,int > mp;int l=nums.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)if (!mp[nums[i]]) mp[nums[i]]++;else return nums[i];return -1 ;
思路3 由于n很小,所以可以开一个大小为100005的数组,用下标维护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 bool vis[100005 ]={0 };int l=nums.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)if (!vis[nums[i]]) vis[nums[i]]=1 ;else return nums[i];return -1 ;
思路4 这个方法不需要额外空间
排序数组,前一个跟后一个一样就重复了啦
1 2 3 4 5 int l=nums.size ();sort (nums.begin (),nums.end ());for (int i=1 ;i<l;i++)if (nums[i-1 ]==nums[i])return nums[i];return -1 ;
思路5 很神奇的原地交换
我的理解是对排序的特殊考虑
首先如果没有重复的那么最后肯定是nums[0]=0,nums[1]=1…,num[n-1]=n-1
所以我们遍历数组,把每个数送回它应该有的位子
送回的过程中有两种情况
1.nums[i]!=i,此时我们让i回家
2.nums[i]==i,说明出现了重复数字
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 int l=nums.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)while (nums[i]!=i) if (nums[nums[i]]==nums[i]) return nums[i];swap (nums[i],nums[nums[i]]);return -1 ;
二维数组中的查找 思路1 这题乍一看,如果数组是一维的就是妥妥的二分了,但变成二维之后就不那么很好做了
首先想到的是枚举每一行,然后对这一行的数字做二分处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int n=matrix.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++)int > ::iterator it=lower_bound (matrix[i].begin (),matrix[i].end (),target);if (it!=matrix[i].end ())if (matrix[i][int (it-matrix[i].begin ())]==target) return 1 ;return 0 ;
思路2 参考了部分题解,发现一个神奇的做法
从右上角开始走,小的往左走,大的往下走(左下角同理)
这两个位子的数有一个特点:比他小的数一定在以它左边那个数为右上角的矩阵里( 就是除掉它本身那一列),比他大的数一定在以它下面那个数为右上角的矩阵里(左下角同理)
所以就等价于一个猜数游戏了
(没想到居然比二分还慢,啊仔细想想确实比二分慢)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 int n=matrix.size ();if (!n) return 0 ;int m=matrix[0 ].size ();int x=0 ,y=m-1 ;while (x<n&&y>=0 )if (matrix[x][y]>target)else if (matrix[x][y]<target)else return 1 ;return 0 ;int n=matrix.size ();if (!n) return 0 ;int m=matrix[0 ].size ();int x=n-1 ,y=0 ;while (x>=0 &&y<m)if (matrix[x][y]>target)else if (matrix[x][y]<target)else return 1 ;return 0 ;
思路3 其实一开始也有想过分治,但好像不知道要怎么分的样子,看了题解写一份
对任意一点,它左上角的点一定比他本身小,右下角的点一定比他本身大
其余两块未知
每次比较一定可以排除一个方块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public :bool so (vector<vector<int >>& matrix,int target,int a,int b,int x,int y) {if (x<a||y<b) return 0 ;int midx=(a+x)/2 ,midy=(b+y)/2 ;if (matrix[midx][midy]==target) return 1 ;else if (matrix[midx][midy]<target)return so (matrix,target,a,midy+1 ,midx,y)||so (matrix,target,midx+1 ,b,x,midy)||so (matrix,target,midx+1 ,midy+1 ,x,y);else return so (matrix,target,a,midy,midx-1 ,y)||so (matrix,target,midx,b,x,midy-1 )||so (matrix,target,a,b,midx-1 ,midy-1 );bool findNumberIn2DArray (vector<vector<int >>& matrix, int target) int n=matrix.size ();if (!n) return 0 ;int m=matrix[0 ].size ();return so (matrix,target,0 ,0 ,n-1 ,m-1 );
注意
分块时要注意边界,不然可能进入死循环(主要是2 * 2和1 * 1的小方块可能会卡死)
替换空格 思路1 最纯朴的想法
1 return s.replace (" " ,"%20" );
当然这就要求你对于string有一定的了解
思路2 手模思路1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public :string replaceSpace (string s) {"" ;int l=s.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)if (s[i]==' ' ) ans+="%20" ;else ans+=s[i];return ans;
从尾到头打印链表 个人认为就这道题而言写递归意义不大还有爆栈的风险
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public :vector<int > reversePrint (ListNode* head) {int > ans;while (head)push_back (head->val);int l=0 ,r=ans.size ()-1 ;while (l<r)swap (ans[l],ans[r]);return ans;
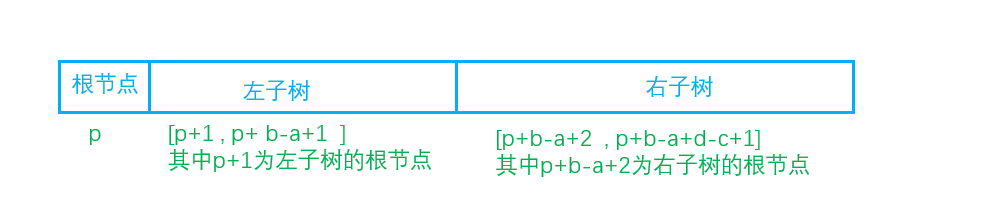
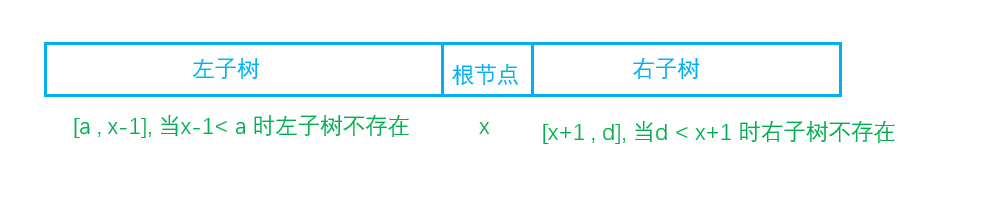
重建二叉树 除了我大家都知道,在一个前序遍历中,遍历顺序为 爹->左儿子 -> 右儿子
所以在preorder数组中应该是这样的
中序遍历顺序为 左儿子-> 爹 -> 右儿子
所以inorder数组是这样的
preorder[p]==inorder[x]
那么我们就可以通过不断划分出他的跟节点、左儿子和右儿子来AC啦!
关于这种代码TreeNode* pa=new TreeNode();pa->val=preorder[p+1];
按照下面的注释来说应该写成TreeNode* pa=new TreeNode(preorder[p+1]);
但
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution {public :int ,int > mp;void bu (vector<int >& preorder, vector<int >& inorder,TreeNode* fa,int p,int a,int b,int c,int d) {if (b<a)NULL ;else new TreeNode ();1 ];int x=mp[preorder[p+1 ]];bu (preorder,inorder,pa,p+1 ,a,x-1 ,x+1 ,b);if (d<c)NULL ;else new TreeNode ();2 ];int x=mp[preorder[p+b-a+2 ]];bu (preorder,inorder,pa,p+b-a+2 ,c,x-1 ,x+1 ,d);return ;TreeNode* buildTree (vector<int >& preorder, vector<int >& inorder) {int l=preorder.size ();if (!l) return NULL ;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)new TreeNode ();0 ];int x=mp[preorder[0 ]];bu (preorder,inorder,ans,0 ,0 ,x-1 ,x+1 ,l-1 );return ans;
关于知道preorder[p]后怎么求x
用map建立inorder数组中每一个数和位置的对应关系
啊上面的代码写的我好难受啊
首先是左右子树的问题,代码冗余太多
然后就是每次传参都要传两个数组就很难受
看了下题解代码
果然是我写丑了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public :TreeNode* buildTree (vector<int >& preorder, vector<int >& inorder) {int l=preorder.size ();if (!l) return NULL ;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)return so (0 ,0 ,l-1 );int > pre;int > ino;int ,int > mp;TreeNode* so (int fa,int l,int r) {if (l>r) return NULL ;new TreeNode (pre[fa]);int x=mp[pre[fa]];so (fa+1 ,l,x-1 );so (fa+x-l+1 ,x+1 ,r);return pa;
用两个栈实现队列 翻了下题目下面的评论发现有很多人吐槽说b不知道 题目想表达什么
栈是后进先出,队列是先进先出
怎么让两个后进先出的栈变成一个先进先出的队列
啊觉得好像说了又觉得没说
emmm
大概就是负负得正的样子
先把数字装栈1里
然后再把栈1倒腾到栈2里
主要是要注意栈为空时不要取数就行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class CQueue {int > s1,s2;public :CQueue () {while (!s1.empty ()) s1.pop ();while (!s2.empty ()) s1.pop ();void appendTail (int value) push (value);int deleteHead () while (!s1.empty ())push (s1.top ());pop ();if (s2.empty ()) return -1 ;int ans=s2.top ();pop ();while (!s2.empty ())push (s2.top ());pop ();return ans;
I. 斐波那契数列 II. 青蛙跳台阶问题 啊典型的递归问题
但数据太水了直接开数组写模拟比较快乐
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public :int mod=1e9 +7 ;long long ans[105 ]={0 };int fib (int n) 1 ]=ans[2 ]=1 ;for (int i=3 ;i<=n;i++)ans[i]=ans[i-1 ]+ans[i-2 ],ans[i]%=mod;return int (ans[n]);class Solution {public :int mod=1e9 +7 ;long long ans[105 ]={0 };int numWays (int n) 0 ]=1 ;1 ]=1 ;2 ]=2 ;for (int i=3 ;i<=n;i++)ans[i]=ans[i-1 ]+ans[i-2 ],ans[i]%=mod;return int (ans[n])%mod;
另一种思路 以斐波那契数列为例
试想当n很大的时候,求斐波那契数列的第n项mod p
从1推到n复杂度为O(n)
复杂度大概在O(8lgn)的样子
POJ好像已经没了
汗
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #define ll long long using namespace std;const int N=2 ;const int mod=1e4 ;int n;void mul (int c[][N],int a[][N],int b[][N]) int tmp[N][N]={0 };for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++)for (int j=0 ;j<N;j++)for (int k=0 ;k<N;k++)memcpy (c,tmp,sizeof (tmp));int main () while (cin>>n)if (n==-1 ) break ;int f0[N][N]={0 ,1 };int a[N][N]={{0 ,1 },{1 ,1 }};while (n)if (n&1 ) mul (f0,f0,a);mul (a,a,a);1 ;0 ][0 ]<<'\n' ;return 0 ;
旋转数组的最小数字 一个思维题的样子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public :int minArray (vector<int >& numbers) int l=numbers.size ();for (int i=1 ;i<l;i++)if (numbers[i]<numbers[i-1 ]) return numbers[i];return numbers[0 ];
机器人的运动范围 bfs就很快乐
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {public :int movingCount (int m, int n, int k) if (k==0 ) return 1 ;bool vis[105 ][105 ]={0 };int st[4 ][2 ]={{1 ,0 },{-1 ,0 },{0 ,1 },{0 ,-1 }};int ans=0 ;struct node int x;int y;push ({0 ,0 });1 ;0 ][0 ]=1 ;while (!q.empty ())int xx,yy;int x=q.front ().x;int y=q.front ().y;pop ();for (int i=0 ;i<4 ;i++)0 ];1 ];if (xx>=0 &&xx<m&&yy>=0 &&yy<n&&!vis[xx][yy]&&(xx%10 +xx/10 +yy/10 +yy%10 )<=k)1 ;push ({xx,yy});return ans;
矩阵中的路径 简单的搜索+剪枝
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Solution {char >> mp;int n,m;bool vis[205 ][205 ];int st[4 ][2 ]={{1 ,0 },{-1 ,0 },{0 ,1 },{0 ,-1 }};bool ans=0 ;void dfs (int x,int y,int num) {if (num==s.size ()) {ans=1 ; return ;}int xx,yy;for (int i=0 ;i<4 &&!ans;i++)0 ];1 ];if (xx>=0 &&xx<n&&yy>=0 &&yy<m&&!vis[xx][yy]&&mp[xx][yy]==s[num])1 ;dfs (xx,yy,num+1 );0 ;public :bool exist (vector<vector<char >>& board, string word) size ();if (!n) return 0 ;0 ].size ();for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++)push_back (board[i]);for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++)for (int j=0 ;j<m;j++)if (board[i][j]==word[0 ])memset (vis,0 ,sizeof (vis));1 ;dfs (i,j,1 );if (ans) return 1 ;return 0 ;
看了下题解比我写的漂亮点
但它跑出来数据没我好看
啊奇怪的好胜心
11~20 剪绳子 众所周知
如果只分一次,对于n,分成n/2和 (n+1)/2最好
分成 1和n-1就很难受
那么我们就可以找到两个最小单位2=1+1,3=2+1
分成3比分成2划算
剩下的就靠代码了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public :int cuttingRope (int n) if (n==2 ) return 1 ;if (n==3 ) return 2 ;if (n%3 ==0 )return pow (3 ,n/3 );if (n%3 ==1 ) return pow (3 ,n/3 -1 )*2 *2 ;return pow (3 ,n/3 )*2 ;
加个快速幂就双倍经验啦
剪绳子2
注意开long long 防止在计算过程中溢出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public :int mod=1e9 +7 ;inline long long ksm (long long a,long long b) {long long ans=1 ;while (b)if (b&1 ) ans*=a,ans%=mod;1 ;return ans;int cuttingRope (int n) if (n==2 ) return 1 ;if (n==3 ) return 2 ;long long nn=n;if (nn%3 ==0 )return ksm (3LL ,nn/3 );if (n%3 ==1 ) return ksm (3LL ,nn/3 -1 )*2 %mod*2 %mod;return ksm (3LL ,nn/3 )*2 %mod;
二进制中1的个数 憨憨只会模拟了,嘤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public :int hammingWeight (uint32_t n) int cnt=0 ;for (int i=0 ;i<33 ;i++)if (n&(1LL <<i)) cnt++;return cnt;
但题解区很精彩啊
神奇的位运算优化
n&(n-1) 可以把n的最低位1变成0
所以可以不断消耗1直到n变成0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public :int hammingWeight (uint32_t n) int cnt=0 ;while (n)-1 );return cnt;
比解1慢
不知道为什么
果然有库函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution {public :int hammingWeight (uint32_t n) return __builtin_popcount(n);
查了资料说是$logn$复杂度,但为什么也比解1慢啊
数值的整数次方 快速幂板子题
注意n可以为负
为负数时把x变为倒数就可以了
但有一组数据
嘻把n变为-n就溢出了
所以要开long long
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :double myPow (double x, int n) double ans=1.0 ;long long nn=n;if (nn<0 )1.0 /x;while (nn)if (nn&1 ) ans*=x;1 ;return ans;
打印从1到最大的n位数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public :vector<int > printNumbers (int n) {int > ans;int r=0 ;while (n--)10 +9 ;for (int i=1 ;i<=r;i++)push_back (i);return ans;
评论区有讨论大数写法
大概就是全排和去除前导零的问题
懒得写了
删除链表的节点 分两种情况
要删除的是头结点
要删除的不是头结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public :ListNode* deleteNode (ListNode* head, int val) {if (head->val==val) return head->next;while (p->val!=val)return head;
表示数值的字符串 觉得应该是一个自动机
但我没学字符串
模拟+面向数据编程
一次AC是我没想到的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 class Solution {bool zs (int l,int r) {if (l>r) return 0 ;if (ss[l]=='+' ||ss[l]=='-' ) l++;if (l>r) return 0 ; while (l<=r)if (ss[l]>='0' &&ss[l]<='9' ) l++;else return 0 ;return 1 ;bool xs (int l,int r) {if (l>r) return 0 ;if (ss[l]=='+' ||ss[l]=='-' ) l++;if (l>r) return 0 ;int x=ss.find ("." );if (x==-1 ) return 0 ;if (x==l) if (l>r) return 0 ;while (l<=r) if (ss[l]>='0' &&ss[l]<='9' ) l++;else return 0 ;return 1 ;else if (x==r)if (l>r) return 0 ;while (l<=r) if (ss[l]>='0' &&ss[l]<='9' ) l++;else return 0 ;return 1 ;else while (l<x)if (ss[l]>='0' &&ss[l]<='9' ) l++;else return 0 ;1 ;while (l<=r)if (ss[l]>='0' &&ss[l]<='9' ) l++;else return 0 ;return 1 ;public :bool isNumber (string s) int l=0 ,r=s.size ()-1 ;while (l<=r&&s[l]==' ' ) l++;while (r>=l&&s[r]==' ' ) r--;if (l>r) return 0 ;transform (s.begin (),s.end (),s.begin (),::tolower);int x=s.find ("e" );if (x!=-1 )if (zs (x+1 ,r)) r=x-1 ;else return 0 ;return zs (l,r)||xs (l,r);
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 双指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public :vector<int > exchange (vector<int >& nums) {int l=0 ,r=nums.size ()-1 ;while (l<r)while (l<=r&&nums[l]%2 ==1 ) l++;while (l<=r&&nums[r]%2 ==0 ) r--;if (l<r) swap (nums[l],nums[r]),l++,r--;return nums;
突发奇想…快乐排序
但他太慢了
注意cmp函数要写在类外
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 bool cmp (int a,int b) {return a%2 >b%2 ;class Solution {public :vector<int > exchange (vector<int >& nums) {sort (nums.begin (),nums.end (),cmp);return nums;
链表中倒数第k个节点 最纯朴的想法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public :ListNode* getKthFromEnd (ListNode* head, int k) {int n=0 ;while (h)while (n--)return head;
题解中的双指针思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public :ListNode* getKthFromEnd (ListNode* head, int k) {while (k--)while (h)return head;
然而跑分没有1高
寄
反转链表 反转链表需要知道前一个节点
反转后需要能找到原本的后一个节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public :ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) {if (head==NULL ||head->next==NULL ) return head;if (ne->next==NULL )NULL ;return ne;NULL ;while (ne)return head;
递归
这里的return只是为了让最后找到那个新的头结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {public :ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) {if (head==NULL ||head->next==NULL ) {ans=head;return ans;}reverseList (head->next);NULL ;return ans;class Solution {inline void so (ListNode* head) {if (!head||!head->next) {ans=head;return ;}so (head->next);NULL ;return ;public :ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) {so (head);return ans;
这个跑分总是很迷
合并两个排序的链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution {public :ListNode* mergeTwoLists (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {if (!l1) return l2;if (!l2) return l1;if (l1->val<l2->val)else while (l1&&l2)if (l1->val<l2->val)else if (l1) ans->next=l1;if (l2) ans->next=l2;return h;
21~30 树的子结构 就硬比呗
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {bool ch (TreeNode* A,TreeNode* B) {if (!B) return 1 ;if (A&&B) if (A->val!=B->val) return 0 ;return ch (A->left,B->left)&&ch (A->right,B->right);return 0 ;public :bool isSubStructure (TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) if (!B||!A) return 0 ;if (ch (A,B)) return 1 ;return isSubStructure (A->left,B)||isSubStructure (A->right,B);
跑分太丑了
翻了以前的提交记录居然跑分还蛮高
虽然写的很丑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {public :bool ans=0 ;bool ch (TreeNode* s,TreeNode* n) {if (!n)return 1 ;if (!s) return 0 ;if (s->val!=n->val) return 0 ;return ch (s->left,n->left)&&ch (s->right,n->right);void dfs (TreeNode* s,TreeNode* B) {if (ans||!s) return ;if (s->val == B->val)ch (s,B);if (ans) return ;dfs (s->left,B);if (ans) return ;dfs (s->right,B);if (ans) return ;bool isSubStructure (TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) if (!B) return 0 ;dfs (A,B);return ans;
二叉树的镜像 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {void dfs (TreeNode* root) {if (!root) return ;swap (root->left,root->right);dfs (root->left);dfs (root->right);public :TreeNode* mirrorTree (TreeNode* root) {dfs (root);return root;
对称的二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {inline bool dfs (TreeNode* a,TreeNode* b) {if (!a&&!b) return 1 ;if (a&&b&&a->val==b->val)return dfs (a->left,b->right)&&dfs (a->right,b->left);return 0 ;public :bool isSymmetric (TreeNode* root) if (!root) return 1 ;return dfs (root->left,root->right);
顺时针打印矩阵 一个简单模拟写了我一天
果然二狗不会数格子
基本上[[1,2,3,4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1]]
和样例跑过去问题就不大了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public :vector<int > spiralOrder (vector<vector<int >>& matrix) {int > ans;int n=matrix.size ();if (!n) return ans;int m=matrix[0 ].size ();for (int i=0 ;i<n&&i<m;i++,n--,m--)for (int j=i;j<=m-1 ;j++) ans.push_back (matrix[i][j]);for (int j=i+1 ;j<=n-2 ;j++) ans.push_back (matrix[j][m-1 ]);if (i!=n-1 )for (int j=m-1 ;j>=i;j--) ans.push_back (matrix[n-1 ][j]);if (i!=m-1 )for (int j=n-2 ;j>=i+1 ;j--) ans.push_back (matrix[j][i]);return ans;
另一种类似于搜索的思路 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {int n,m;bool vis[105 ][105 ]={0 };bool ch (int x,int y) {return x>=0 &&x<n&&y>=0 &&y<m&&!vis[x][y];public :vector<int > spiralOrder (vector<vector<int >>& matrix) {int > ans;size ();if (!n) return ans;0 ].size ();int x=0 ,y=0 ;push_back (matrix[x][y]);1 ;while (ans.size ()<n*m)while (ch (x,++y)) ans.push_back (matrix[x][y]),vis[x][y]=1 ;while (ch (++x,y)) ans.push_back (matrix[x][y]),vis[x][y]=1 ;while (ch (x,--y)) ans.push_back (matrix[x][y]),vis[x][y]=1 ;while (ch (--x,y)) ans.push_back (matrix[x][y]),vis[x][y]=1 ;return ans;
包含min函数的栈 单调栈板子题
开两个栈s1,s2
s1为正常栈,模拟push和pop
s2为单调栈,只有当前值小于等于 栈顶时才入栈
弹出时若s1,s2栈顶数值相同则一起弹出,否则就只弹出s1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class MinStack {int > s1,s2;public :MinStack () {void push (int x) push (x);if (s2.empty ()||s2.top ()>=x)push (x);void pop () if (s1.top ()==s2.top ()) s2.pop ();pop ();int top () return s1.top ();int min () return s2.top ();
栈的压入、弹出序列 直接模拟
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public :bool validateStackSequences (vector<int >& pushed, vector<int >& popped) int l=pushed.size ();if (l!=popped.size ()) return 0 ;int ,int > mp;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)int > s;int a=0 ,b=0 ;for (;b<l;b++)if (!s.empty ()&&popped[b]==s.top ()) s.pop ();else int x=mp[popped[b]];if (x>=a)while (x>=a)push (pushed[a]),a++;pop ();else return 0 ;return 1 ;
跑分太丑了,优化一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public :bool validateStackSequences (vector<int >& pushed, vector<int >& popped) int l=pushed.size ();if (l!=popped.size ()) return 0 ;int > s;int a=0 ,b=0 ;while (b<l)if (!s.empty ()&&popped[b]==s.top ()) s.pop (),b++;else if (a>=l) return 0 ;while (a<l&&(s.empty ()||s.top ()!=popped[b])) s.push (pushed[a]),a++;return s.empty ();
II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II bfs一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {struct node {int st;public :int >> levelOrder (TreeNode* root) {int >> ans;int > a;if (!root) return ans;int cnt=1 ;push ({root,1 });while (!q.empty ())if (q.front ().num->left) q.push ({q.front ().num->left,q.front ().st+1 });if (q.front ().num->right) q.push ({q.front ().num->right,q.front ().st+1 });if (q.front ().st==cnt) a.push_back (q.front ().num->val);else push_back (a);clear ();push_back (q.front ().num->val);pop ();if (a.size ()) ans.push_back (a);return ans;
III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III 把上一题代码改一下
行数为偶数时就将这一层倒置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution {struct node {int st;public :int >> levelOrder (TreeNode* root) {int >> ans;int > a;if (!root) return ans;int cnt=1 ;push ({root,1 });while (!q.empty ())if (q.front ().num->left) q.push ({q.front ().num->left,q.front ().st+1 });if (q.front ().num->right) q.push ({q.front ().num->right,q.front ().st+1 });if (q.front ().st==cnt) a.push_back (q.front ().num->val);else push_back (a);clear ();push_back (q.front ().num->val);pop ();if (a.size ()) ans.push_back (a);int l=ans.size ();for (int i=1 ;i<l;i+=2 )int ll=0 ,rr=ans[i].size ()-1 ;while (ll<rr)swap (ans[i][ll],ans[i][rr]),ll++,rr--;return ans;
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 递归
但总觉得写的很丑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {bool so (vector<int >& p,int l,int r) {if (l+1 >=r) return 1 ;int x=l;while (x<=r)if (p[x]>=p[r]) break ;for (int i=l;i<x;i++) if (p[i]>=p[r] ) return 0 ;for (int i=x;i<r;i++) if (p[i]<=p[r] ) return 0 ;return so (p,l,x-1 )&&so (p,x,r-1 );public :bool verifyPostorder (vector<int >& postorder) int l=postorder.size ();if (l<=1 ) return 1 ;return so (postorder,0 ,l-1 );
看到题解有个用单调栈写的,先挂这里有空来补
二叉树中和为某一值的路径 跑一遍dfs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution {int >> ans;int > a;int sum;int t;void dfs (TreeNode* root) {if (!root->left&&!root->right)if (sum==t) ans.push_back (a);return ;if (root->left)push_back (root->left->val);dfs (root->left);pop_back ();if (root->right)push_back (root->right->val);dfs (root->right);pop_back ();public :int >> pathSum (TreeNode* root, int target) {if (!root) return ans;push_back (root->val);dfs (root);return ans;
31~40 复杂链表的复制 用map在新旧节点间产生一一对应的关系
然后直接模拟连线
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {public :Node* copyRandomList (Node* head) {if (!head) return NULL ;while (h)new Node (0 );while (head)return h;
二叉搜索树与双向链表 二叉搜索树的中序遍历即为要的答案
设p为当前节点,pre为之前遍历的节点,有
p->left=pre;
if(pre) pre->right=p;
最后记得首尾连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {void dfs (Node* p) {if (!p) return ;dfs (p->left);if (pre) pre->right=p;dfs (p->right);public :Node* treeToDoublyList (Node* root) {if (!root) return root;while (head->left) head=head->left;while (tail->right) tail=tail->right;dfs (root);return head;
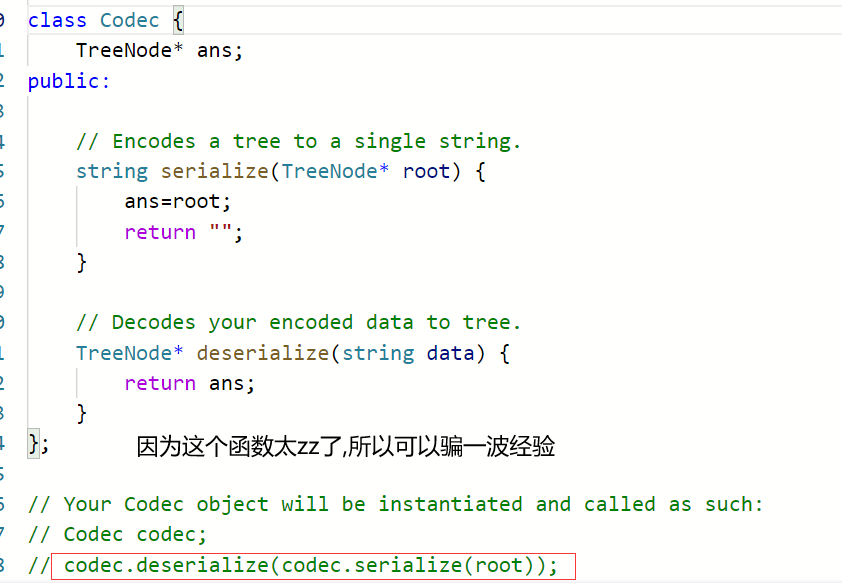
序列化二叉树 看起来题目很复杂,但是实际上就是叫你用string 去存储一棵二叉树,并把他还原
思路
把空节点看成一个特殊字符,这样就可以用string存储一棵满二叉树
先序中序后序甚至层序都可以做到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 class Codec {void dfs (TreeNode* fa) {if (!fa)"# " ;return ;to_string (fa->val)+" " ;dfs (fa->left);dfs (fa->right);inline int tu () {int x=0 ,l=ans.size ();bool f=0 ;int i=0 ;if (ans[0 ]=='-' ) f=1 ,i++;for (;i<l;i++) 10 +ans[i]-'0' ;if (f) x*=-1 ;return x;void dd (TreeNode* p) {if (!p) return ;if (ans!="#" )new (TreeNode);tu ();dd (p->left);if (ans!="#" )new (TreeNode);tu ();dd (p->right);return ; public :string serialize (TreeNode* root) {dfs (root);return ans;TreeNode* deserialize (string data) {new (TreeNode);if (ans=="#" ) return NULL ;tu ();dd (a);return a;
浪一下
字符串的排列 stl yyds
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public :vector<string> permutation (string s) {char c[10 ]={0 };int l=s.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++) c[i]=s[i];sort (c,c+l);do {push_back (string (c));while (next_permutation (c,c+l));return ans;
不用stl的话可以考虑dfs或bfs
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Solution {public :int majorityElement (vector<int >& nums) sort (nums.begin (),nums.end ());return nums[nums.size ()/2 ];
神奇的摩尔投票
只能找到出现次数超过一半的数字,不能找众数
出现不同的就消掉,最后留一下来的就是答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public :int majorityElement (vector<int >& nums) int ve=1 ,ans=nums[0 ];for (int i=1 ;i<nums.size ();i++)if (ve==0 ) ans=nums[i],ve=1 ;else if (nums[i]!=ans) ve--;else ve++;return ans;
最小的k个数 快乐排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public :vector<int > getLeastNumbers (vector<int >& arr, int k) {sort (arr.begin (),arr.end ());int > ans;for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++)push_back (arr[i]);return ans;
优先队列
虽然看起来很高级的样子,但觉得并没有比sort好用多少(至少跑分是这样的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :vector<int > getLeastNumbers (vector<int >& arr, int k) {int > ans;if (k)int ,vector<int > > q;for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++)push (arr[i]);for (int i=k;i<arr.size ();i++)if (arr[i]<q.top ()) q.pop (),q.push (arr[i]);while (!q.empty ())push_back (q.top ()),q.pop ();return ans;
数据流中的中位数 插入排序卡过去了
觉得没卡时间啊
就是数据很不好看罢了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class MedianFinder {int > a;public :MedianFinder () {void addNum (int num) if (!a.size ()) a.push_back (num);else a.insert (lower_bound (a.begin (),a.end (),num),num);double findMedian () int l=a.size ();if (!l) return double (NULL );if (l%2 ==0 ) return (a[l/2 ]+a[(l-1 )/2 ])*1.0 /2 ;else return a[(l-1 )/2 ];
用优先队列维护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class MedianFinder {int ,vector<int >, greater<int > >big;int ,vector<int >, less<int > >sma;public :MedianFinder () {void addNum (int num) if (big.size ()>sma.size ()) sma.push (num);else big.push (num);while (big.size ()&&sma.size ()&&big.top ()<sma.top ())push (sma.top ());pop ();push (big.top ());pop ();double findMedian () if (big.size ()==sma.size ()) return (big.top ()+sma.top ())*1.0 /2 ;else if (big.size ()>sma.size ()) return big.top ();return sma.top ();
连续子数组的最大和 当目前的sum<0时是对后面没有贡献的,只要当前值大于sum就可以把他替换掉( 当sum<num[i] <0 时, ans不会被替换 ,直到遇到比a 大的就会丢弃当前a 并继续去和ans比较 )
否则就加上
不断更新ans
有点dp的感觉
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public :int maxSubArray (vector<int >& nums) int a;int n=nums.size ();0 ];int ans=a;for (int i=1 ;i<n;i++)if (a<0 ) a=max (nums[i],a);else max (ans,a);return ans;
1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数 按每一位推式子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public :int countDigitOne (int n) long long a[15 ]={0 };1 ]=1 ;for (long long i=2 ,j=10 ;i<10 ;i++,j*=10 ) a[i]=j*i;long long cnt=1 ,p=1 ,xx=0 ;long long sum[15 ]={0 };while (n)long long x=n%10 ;10 ;if (x==0 ) sum[cnt]=sum[cnt-1 ];else if (x==1 )1 +sum[cnt-1 ]+a[cnt-1 ];else sum[cnt]=p+x*a[cnt-1 ]+sum[cnt-1 ];10 ;return sum[cnt-1 ];
把数组排成最小的数 继续快乐sort
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 bool cmp (string a,string b) return a+b<b+a;class Solution {public :string minNumber (vector<int >& nums) {for (int i=0 ;i<nums.size ();i++)push_back (to_string (nums[i]));sort (s.begin (),s.end (),cmp);for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++)return ans;
41~50 数字序列中某一位的数字 数数
相同位数的数字和可以算出来
然后可以找到是某个数的第几位数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public :int findNthDigit (int n) if (n<10 ) return n;long long a[10 ]={0 };1 ]=9 ;for (long long i=2 ,j=90 ;i<10 ;i++,j*=10 )-1 ];int ans=0 ;int x=lower_bound (a,a+10 ,n)-a;if (n==a[x])for (int i=1 ;i<x;i++)10 +9 ;else -1 ];for (int i=1 ;i<x;i++)10 +9 ;if (n%x==0 ) ans=ans%10 ;else to_string (ans+1 );-1 ]-'0' ;return ans;
把数字翻译成字符串 简单dp
计$f(n)$为num前n个数字构成的答案
当第n个数字和第n-1个数字构成的两位数不超过25时,说明可以由前n-2个数字和后两个数字构成答案
由前n-1个数字和第n个数字一定能构成答案
和上台阶思路类似,不太明白为什么上台阶是简单但这题是中等…
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public :int translateNum (int num) to_string (num);long long ans[20 ]={0 };int l=s.size ();0 ]=1 ;if (l>1 )if ((s[0 ]-'0' )*10 +(s[1 ]-'0' )<26 &&s[0 ]!='0' ) ans[1 ]=2 ;else ans[1 ]=1 ;for (int i=2 ;i<l;i++)if ((s[i-1 ]-'0' )*10 +(s[i]-'0' )<26 &&s[i-1 ]!='0' ) ans[i]+=ans[i-2 ];-1 ];return ans[l-1 ];
礼物的最大价值 简单dp
从右下角的格子开始往上推
每个非边界的格子有两种走法: 向上或者向左
选大的那个就行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :int maxValue (vector<vector<int >>& grid) int m=grid.size (),n=grid[0 ].size ();for (int i=m-1 ;i>=0 ;i--)for (int j=n-1 ;j>=0 ;j--)if (i==m-1 &&j==n-1 ) continue ;if (i==m-1 ) grid[i][j]+=grid[i][j+1 ];else if (j==n-1 ) grid[i][j]+=grid[i+1 ][j];else max (grid[i+1 ][j],grid[i][j+1 ]);return grid[0 ][0 ];
最长不含重复字符的子字符串 暴力
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public :int lengthOfLongestSubstring (string s) int l=s.size ();if (!l) return 0 ;int ans=0 ;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)bool vis[130 ]={0 };int cnt=0 ;for (int j=i;j<l;j++)if (vis[s[j]]) break ;1 ;max (ans,cnt);return ans;
dp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public :int lengthOfLongestSubstring (string s) int l=s.size ();if (!l) return 0 ;int ans=1 ;int num[130 ];for (int i=0 ;i<130 ;i++) num[i]=-1 ;int dp[40005 ]={0 };0 ]]=0 ;0 ]=1 ;for (int i=1 ;i<l;i++)if (num[s[i]]<0 ) dp[i]=dp[i-1 ]+1 ;else if (i-num[s[i]]<=dp[i-1 ]) dp[i]=i-num[s[i]];else dp[i]=dp[i-1 ]+1 ;max (ans,dp[i]);return ans;
丑数 第一反应是类似于素筛之类的东西,但范围超了
小根堆(觉得很暴力)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {long long , vector<long long >,greater<long long > > q;long long > s;public :int nthUglyNumber (int n) if (n<2 )return n;long long ans;push (1 );insert (1 );while (n--)top ();if (!s.count (ans*2 )) s.insert (ans*2 ),q.push (ans*2 );if (!s.count (ans*3 )) s.insert (ans*3 ),q.push (ans*3 );if (!s.count (ans*5 )) s.insert (ans*5 ),q.push (ans*5 );pop ();return ans;
dp
注意相等时的情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {int >dp;int p2,p3,p5;int minn (int a,int b,int c) {if (a<=b&&a<=c) if (a==b) p3++;if (a==c) p5++;return a;if (b<=a&&b<=c) if (a==b) p3++;if (b==c) p5++;return b;if (c==b) p3++;if (a==c) p5++;return c;public :int nthUglyNumber (int n) if (n<2 ) return n;0 ;push_back (1 );while (n--)push_back (minn (dp[p2]*2 ,dp[p3]*3 ,dp[p5]*5 ));return dp[dp.size ()-1 ];
数组中的逆序对 归并排序,翻了个远古时期的班子套上去了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {int cnt;int t[ 50005 ]={0 };void merge_sort (vector<int >& a, int x, int y) if (y - x > 1 )int m = x + (y - x) / 2 ;int p = x, q = m, i = x;merge_sort (a, x, m);merge_sort (a, m, y);while (p < m || q < y)if (q >= y || (p < m && a[p] <= a[q]))else for (i = x; i < y; i++)public :int reversePairs (vector<int >& nums) 0 ;merge_sort (nums,0 ,nums.size ());return cnt;
两个链表的第一个公共节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public :ListNode *getIntersectionNode (ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {while (a!=b)if (a==NULL ) a=headB;else a=a->next;if (b==NULL ) b=headA;else b=b->next;return a;
I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I 1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution {public :int search (vector<int >& nums, int target) return upper_bound (nums.begin (),nums.end (),target)-lower_bound (nums.begin (),nums.end (),target);
II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字 异或
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public :int missingNumber (vector<int >& nums) int ans=0 ;int n=nums.size ();for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++)-1 ];return ans;
二叉搜索树的第k大节点 按照 右儿子-> 父节点 -> 左儿子的顺序遍历树,得到递减序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {int cnt,ans;void dfs (TreeNode* fa) {if (!fa||cnt<=0 ) return ;dfs (fa->right);if (cnt==0 )return ;dfs (fa->left);public :int kthLargest (TreeNode* root, int k) dfs (root);return ans;
51~60 I. 二叉树的深度 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public :int maxDepth (TreeNode* root) if (!root) return 0 ;return max (maxDepth (root->left),maxDepth (root->right))+1 ;
II. 平衡二叉树 跟上一题思路差不多,边跑边比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {bool f=1 ;int so (TreeNode* root) {if (!root) return 0 ;int l=so (root->left)+1 ;int r=so (root->right)+1 ;if (abs (l-r)>1 ) 0 ;return 0 ;return max (l,r);public :bool isBalanced (TreeNode* root) so (root);return f;
I. 数组中数字出现的次数 当 a!= b 时,必有 a^b!=0
我们知道如果只有一个数字出现一次其他数字出现两次时,可以直接异或
有两个时可以分成两组,使这两个答案分别在两组里面,然后异或就可以求出来了
怎么分组
首先把数组异或一遍得到 a^b
a^b!=0 假设某一位$x_i=1$
那么 a ,b 中一定有一个数 $x_i=1$ 而且另一位$x_i!=1$
将nums中的数按$x_i$位是否为1分组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public :vector<int > singleNumbers (vector<int >& nums) {int a=0 ,l=nums.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++) a^=nums[i];int x=1 ,b=0 ;while (1 )if (x&a) break ;1 ;0 ;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)if (nums[i]&x) a^=nums[i];else b^=nums[i];int > ans;push_back (a);push_back (b);return ans;
II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public :int singleNumber (vector<int >& nums) long long ans=0 ;for (long long a=1 ,i=0 ;i<32 ;i++,a <<=1 )int cnt=0 ;for (int j=0 ;j<nums.size ();j++)if (nums[j]&a) cnt++;if (cnt%3 ) ans|=a;return ans;
和为s的两个数字 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public :vector<int > twoSum (vector<int >& nums, int target) {int r=nums.size ();int >ans;int l=0 ;while (l<r)if (nums[l]+nums[r]>target) r--;else if (nums[l]+nums[r]<target) l++;else push_back (nums[l]);push_back (nums[r]);break ;return ans;
II. 和为s的连续正数序列 需要找出 l,r
枚举l 由求和公式算出有没有合适的r
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public :int >> findContinuousSequence (int target) {int >> ans;for (long long l=1 ;l<=(target+1 )/2 ;l++)double x=4 *l*l-4 *l+1 +8 *target;bool f=0 ;long long r=sqrt (x);if (sqrt (x)==r&&r%2 ==1 )-1 )/2 ,f=1 ;if (f)int > a;for (int i=l;i<=r;i++) a.push_back (i);push_back (a);return ans;
I. 翻转单词顺序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public :string reverseWords (string s) {stringstream ss (s) ;while (ss>>a)" " ;return ans;
II. 左旋转字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public :string reverseLeftWords (string s, int n) {int l=s.size ();"" ;for (int i=n;i<l;i++)for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++)return ans;
I. 滑动窗口的最大值 线段树板子题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution {int > maxx;inline int ls (int p) return 2 *p+1 ; }inline int rs (int p) return 2 *p+2 ; }inline void push_up (int id) {max (maxx[ls (id)],maxx[rs (id)]);return ;void build (int l,int r,int id,vector<int >& nums) {if (l==r)return ;build (l,(l+r)>>1 ,ls (id),nums);build (((l+r)>>1 )+1 ,r,rs (id),nums);push_up (id);int qu (int L,int R,int l,int r,int id) if (L<=l&&r<=R)return maxx[id];int mid=(l+r)>>1 ;int ans=INT_MIN;if (L<=mid) ans=max (qu (L,R,l,mid,ls (id)),ans);if (R>mid) ans=max (qu (L,R,mid+1 ,r,rs (id)),ans);return ans;public :vector<int > maxSlidingWindow (vector<int >& nums, int k) {int > ans;if (nums.size ()==0 ) return ans;resize (nums.size ()*4 +5 );build (0 ,nums.size ()-1 ,0 ,nums);for (int i=0 ;i+k-1 <nums.size ();i++)push_back (qu (i,i+k-1 ,0 ,nums.size ()-1 ,0 ));return ans;
但是为什么数据这么难看捏
奥原来是我写丑了
单调队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 struct no {int num,id;struct cmp {bool operator () (no a,no b) {if (a.num==b.num) return a.id>b.id;return a.num<b.num;class Solution {public :vector<int > maxSlidingWindow (vector<int >& nums, int k) {int > ans;int l=nums.size ();if (!l) return ans;for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++) q.push ({nums[i],i});push_back (q.top ().num);for (int i=k;i<l;i++)push ({nums[i],i});while (q.top ().id<=i-k) q.pop ();push_back (q.top ().num);return ans;
II. 队列的最大值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class MaxQueue {int > q1;int > q2;public :MaxQueue () {int max_value () if (q1.empty ()) return -1 ;return q2.front ();void push_back (int value) while (!q2.empty ()&&q2.back ()<value) q2.pop_back ();push_back (value);push (value);int pop_front () if (q1.empty ()) return -1 ;int x=q1.front ();pop ();if (q2.front ()==x) pop_front ();return x;
61~70 n个骰子的点数 有点背包的感觉
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public :vector<double > dicesProbability (int n) {double > ans;double dp[70 ]={0 };double p=1.0 /6 ;for (int i=1 ;i<=6 ;i++) dp[i]=p;for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++)for (int j=i*6 ;j>=i;j--)0 ;for (int k=j-1 ;k>=j-6 &&k>0 ;k--)6 ;for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) dp[j] = 0 ;for (int i=n;i<=n*6 ;i++) ans.push_back (dp[i]);return ans;
扑克牌中的顺子 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :bool isStraight (vector<int >& nums) sort (nums.begin (),nums.end ());int cnt=0 ;while (cnt<5 &&nums[cnt]==0 ) cnt++;if (cnt>=4 ) return 1 ;if (nums[4 ]-nums[cnt]>4 ) return 0 ;bool vis[15 ]={0 };for (;cnt<5 ;cnt++) if (vis[nums[cnt]]) return 0 ;1 ;return 1 ;
圆圈中最后剩下的数字 模拟超时了,寄
以前一直以为约瑟夫环是给小朋友连模拟的
小朋友竟是我自己
倒推法解题
最后一个剩余的一定是0号(数组从0开始)
那么在倒数第二轮时,他的id应该是(id+m)%2
倒数第三轮 (idd+m)%3
好耶!
ps: lc不开会员判题是真的慢
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public :int lastRemaining (int n, int m) int ans=0 ;for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++)return ans;
股票的最大利润 用数组记录每个数后面最大的数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public :int min (int a,int b) return a<b? a:b;int max (int a,int b) return a>b? a:b;int maxProfit (vector<int >& prices) int l=prices.size ();int ans=0 ,minn=INT_MAX;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)min (minn,prices[i]);max (ans,prices[i]-minn);return ans;
求1+2+…+n 大概就是写题写累了图一乐呵
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Solution {public :int sumNums (int n) bool a[n][n+1 ];return sizeof (a)>>1 ;
不用加减乘除做加法 一看就是位运算
一看就不会QAQ
和 sum=a^b
进位 c=(a&b)<<1;
ans=sum+c
差不多就是这样
注意,c++中负数不支持左移,所以要转化为unsigned int
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Solution {public :int add (int a, int b) if (b==0 ) return a;return add ( a^b, int ((unsigned int )(a&b)<<1 ) );
构建乘积数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public :vector<int > constructArr (vector<int >& a) {int > ans;int l=a.size ();resize (l);int x=1 ;for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)1 ;for (int i=l-1 ;i>=0 ;i--)return ans;
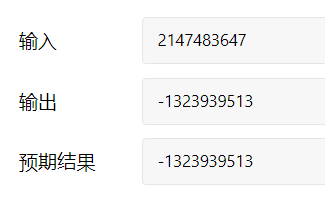
把字符串转换成整数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public :int strToInt (string str) long long ans=0 ;int l=str.size ();int i=0 ;while (i<l&&str[i]==' ' ) i++;if (i==l) return 0 ;int f=1 ;if (str[i]=='-' ) f=-1 ,i++;else if (str[i]=='+' ) i++;else if (str[i]>='0' &&str[i]<='9' );else return 0 ;while (i<l&&str[i]>='0' &&str[i]<='9' )10 +str[i]-'0' ;if (f==1 &&ans>INT_MAX) return INT_MAX;if (f==-1 &&ans>INT_MAX+1LL ) return INT_MIN;return ans*f;
I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 只查一次…为什么要写lca(还tm写tle了)
嘤
二叉搜索树啊,可以直接知道大小那种啊
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public :TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {while (1 )if (root->val>p->val&&root->val>q->val) root=root->left;else if (root->val<p->val&&root->val<q->val) root=root->right;else break ;return root;
II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 没有数据范围就很难受
29/31 寄
烦死了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public :int ,TreeNode*> mp;int ,bool > vis;void dfs (TreeNode* fa) {if (fa->left) dfs (fa->left);if (fa->right)dfs (fa->right);TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {dfs (root);while (p!=root)1 ;1 ;while (!vis[q->val]) q=mp[q->val];return q;
为什么数据这么丑啊
我明明优化了啊
//没太看明白官方题解里面&&(ls||rs)是干什么的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {bool dfs (TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if (!root) return 0 ;bool ls=dfs (root->left,p,q);bool rs=dfs (root->right,p,q);if ((ls&&rs)||(root->val==p->val||root->val==q->val)) ans=root;return ls||rs||root->val==p->val||root->val==q->val;public :TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {dfs (root,p,q);return ans;
71~74 正则表达式匹配 f[i] [j] S前个与P前j个能否匹配
不考虑 “*” 时
f[i] [j] = f[i-1] [j-1] // s[i] == p[j] || p[j] == ' . '
考虑” * “时
f[i] [j] = f[i] [j-2] || f[i-1] [j] // c* 不重复和重复的情况
边界处理
dp[0] [0] =1; //空串和空正则
dp[0] [n]=? ; //空串和非空正则
dp[n] [0] =0; //非空串和空正则
一开始数组开的1005 * 1005的,跑分很难看,大胆点改成105 * 105后就很nice了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {bool dp[105 ][105 ]={0 };public :bool isMatch (string s, string p) int ls=s.size (),lp=p.size ();for (int i = 0 ; i <= ls; i++)for (int j = 0 ; j <= lp; j++)if (i == 0 && j == 0 ) dp[i][j] = 1 ;else if (j == 0 ) dp[i][j] = 0 ;else {if (p[j - 1 ] != '*' )if (i > 0 && (s[i - 1 ] == p[j - 1 ] || p[j - 1 ] == '.' )) 1 ][j - 1 ];else if (j >= 2 ) dp[i][j] |= dp[i][j - 2 ];if ((j >= 2 ) && (i > 0 ) && (s[i - 1 ] == p[j - 2 ] || p[j - 2 ] == '.' )) dp[i][j] |= dp[i - 1 ][j];return dp[ls][lp];
I. 从上到下打印二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public :vector<int > levelOrder (TreeNode* root) {int >ans;push (root);while (!q.empty ()&&q.front ())push_back (q.front ()->val);if (q.front ()->left) q.push (q.front ()->left);if (q.front ()->right) q.push (q.front ()->right);pop ();return ans;
第一个只出现一次的字符 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public :char firstUniqChar (string s) bool vis[30 ]={0 };int l=s.size ();for (int i=0 ;i<l;i++)if (!vis[s[i]-'a' ]&&s.find (s[i],i+1 )==-1 ) return s[i];'a' ]=1 ;return ' ' ;
 |
| |
|